There are four types of spinal fractures; Compression, Burst, Flexion-distraction, and Fracture-dislocation.
1. Compression Fracture is common in patients with osteoporosis, osteopenia, bone cancer, or patients with other cancers undergoing chemotherapy or radiation. The vertebra is thin, weak, and brittle. Blunt force or extreme pressure may cause the bone to fracture. One type of compression fracture is the wedge when the anterior part of the vertebrae collapses creating a triangular shape.
2. Burst Fracture occur when the vertebrae are crushed by forces such as a car accident. It usually occurs in multiple places causing bony pieces to move around into the spinal cord or other soft tissues. These are the hardest to repair and result in the most damage.
3. Flexion-distraction fractures occur when the body is pushed forward suddenly like when a sudden stop occurs or a car crash. Depending on the degree of force, the vertebra or vertebrae may break. These usually occur in the middle and posterior regions of the vertebrae.
4. Fracture-dislocation results when the entire vertebra from front to back is fractured enough for it to move back and forth or side to side, which is a very unstable situation.
Spinal Fractures

What is a Spinal Fracture?
As the name implies, a spinal fracture is a break in a bone or bones of the spine. This can cause vertebrae to collapse or break. The bone does not have to break in half. Trauma such as car accidents, diving into shallow water, falls, or sporting injuries can cause spinal fractures.
Osteoporosis or osteopenia from lack of hormones, aging, or cancer can cause the bones to collapse inward due to weakness. In these cases, coughing or sneezing can cause a break. Millions of patients suffer from spinal fractures annually with vertebral compression fractions most frequently reported. To compare, spinal fractures are about twice as common compared to hip fractures.
Osteoporosis or osteopenia from lack of hormones, aging, or cancer can cause the bones to collapse inward due to weakness. In these cases, coughing or sneezing can cause a break. Millions of patients suffer from spinal fractures annually with vertebral compression fractions most frequently reported. To compare, spinal fractures are about twice as common compared to hip fractures.
Patient Education Video
What are the Types of Spinal Fractures?
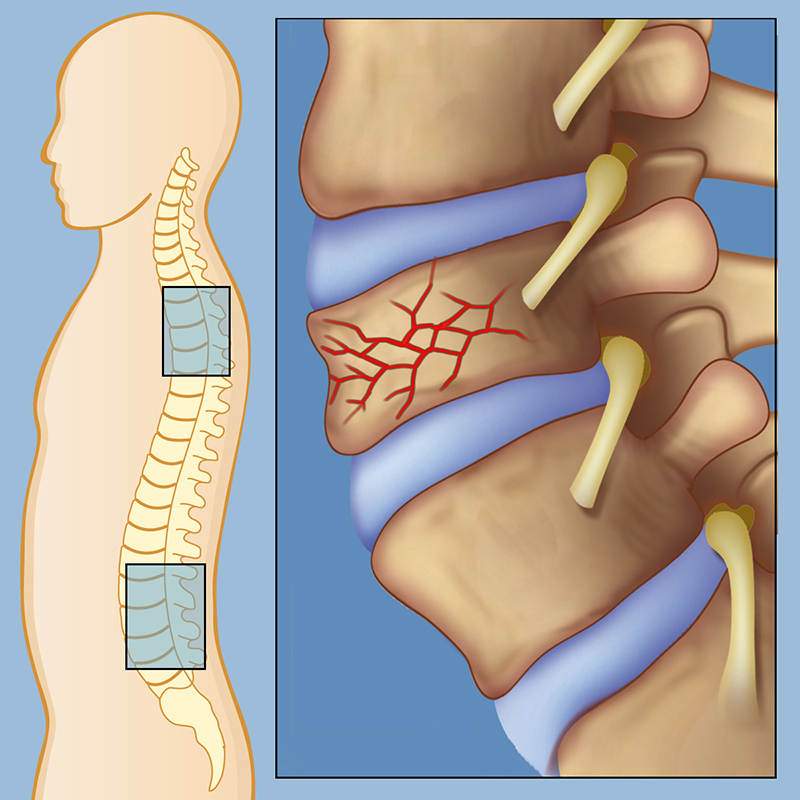
This is an example of a compression fracture.
Each of these types is then categorized as stable, unstable, minor, or major:
a. Stable fractures do not cause nerve problems or spinal deformities. It can usually carry the body weight well enough to be called stable.
b. Unstable fractures are more serious because they can cause serious nerve damage or paralysis. Spinal deformities are possible.
c. Minor fracture means a part of the back side of the vertebra is broken. These include the spinous processes and facet joints which are not as crucial for spinal column stability.
d. Major fractures is a result of damage or fracture to the vertebral body, the pedicles, or the lamina. The vertebral body is responsible for weight bearing and the distribution of force during movement with the vertebrae lining up correctly. If the vertebrae do not line up symmetrically or the pedicles or lamina are broken, there is an increased possibility of nerve damage and instability.
Classification of fractures can be further defined by location such as the thoracic, lumbar or thoracolumbar regions of the spine. It also divides the spine fracture into the back, middle or front regions.
b. Unstable fractures are more serious because they can cause serious nerve damage or paralysis. Spinal deformities are possible.
c. Minor fracture means a part of the back side of the vertebra is broken. These include the spinous processes and facet joints which are not as crucial for spinal column stability.
d. Major fractures is a result of damage or fracture to the vertebral body, the pedicles, or the lamina. The vertebral body is responsible for weight bearing and the distribution of force during movement with the vertebrae lining up correctly. If the vertebrae do not line up symmetrically or the pedicles or lamina are broken, there is an increased possibility of nerve damage and instability.
Classification of fractures can be further defined by location such as the thoracic, lumbar or thoracolumbar regions of the spine. It also divides the spine fracture into the back, middle or front regions.
What Are the Symptoms of a Spinal Fracture?
Symptoms of a spinal fracture are sudden onset back pain that often lasts many days. Pain with ambulation, numbness, tingling, inability to move a limb or feel a limb are particularly serious signs.
- weakness in arms or legs
- numbness in arms or legs
- pain that radiates down the arms or legs (radiculopathy)
- difficulty walking or moving
- bowel/bladder problems- unable, poor urine stream, loss of control
- paralysis (rarely)
What are the Consequences of Untreated Spinal Fractures?
If a spinal fracture is left untreated, the vertebra may heal abnormally or in a bent position, leading to curvatures that can affect internal organs and outward appearances such as hunchback. Spinal alignment is disturbed which puts stress on other joints and muscles. Posture is strained or causes pain with walking or lifting.
- Reduced mobility, loss of balance, and increased risk of falls
- Reduced ability to take care of yourself
- Reduced activity and more bedrest
- Decreased appetite and sleep disorders
- Chronic back pain and fatigue
- Decreased quality of life
- Feelings of isolation and sadness
- Increased risk of future fracture
How are Spinal Fractures Treated?
Conservative treatment with bedrest, NSAIDs, cold packs and hot packs, and other analgesics depending on surrounding damage are the first types of remedies in the case of stable and minor fractures. Exercise, weight loss, and physical therapy after recovery are essential.
Balloon kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure that utilizes a balloon to lift the vertebrae creating a cavity for the bone glue to hold the bones together.
Vertebroplasty is a minimally invasive procedure that utilizes liquid bone cement that is injected into the affected vertebrae which stabilize the fracture and relieves pain.
Balloon kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive procedure that utilizes a balloon to lift the vertebrae creating a cavity for the bone glue to hold the bones together.
Vertebroplasty is a minimally invasive procedure that utilizes liquid bone cement that is injected into the affected vertebrae which stabilize the fracture and relieves pain.
Surgery & Treatment for Spinal Fractures
At Spine Connection we have regenerative and surgical treatments for all spine conditions. As every case is unique we encourage you to receive and compare opinions from our Neurosurgeon and Orthopedic Spine Specialists. We are here to help.
Begin My Assessment
Ask Our Doctors
Join Our Youtube Channel
Watch videos showcasing the latest technologies and surgery techniques, and keep up to date with patient stories from around the globe.