Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS)

What is Ankylosing Spondylitis?
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is arthritis caused by chronic inflammation. It affects the spine and sacroiliac joints. The sacroiliac (SI) joints are the connections between the tailbone and the hips.
AS causes significant joint pain, movement disabilities, and stiffness. It can also be associated with other arthritic conditions that affect the limbs, feet, and hand joints otherwise known as the peripheral joints. Psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, and inflammation of the uvea (outer portion of the eye such as the iris) can be associated with AS.
Sometimes it’s referred to as an autoimmune disease, however unless autoantibodies can be detected, the term autoimmune should not be used to describe AS.
AS can be progressive and is presently incurable, but the symptoms can be treated medically and sometimes surgically. Advanced regenerative therapies can deliver promising results for damaged spinal joints and systemic autoimmune regulation, reducing the ongoing inflammatory cycle AS patients suffer from. With early diagnosis and proper medical care, AS is manageable.
AS causes significant joint pain, movement disabilities, and stiffness. It can also be associated with other arthritic conditions that affect the limbs, feet, and hand joints otherwise known as the peripheral joints. Psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, and inflammation of the uvea (outer portion of the eye such as the iris) can be associated with AS.
Sometimes it’s referred to as an autoimmune disease, however unless autoantibodies can be detected, the term autoimmune should not be used to describe AS.
AS can be progressive and is presently incurable, but the symptoms can be treated medically and sometimes surgically. Advanced regenerative therapies can deliver promising results for damaged spinal joints and systemic autoimmune regulation, reducing the ongoing inflammatory cycle AS patients suffer from. With early diagnosis and proper medical care, AS is manageable.
Diagnosis of Ankylosing Spondylitis
The condition of AS can be confused with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) which some believe is an early version of AS. Different criteria have been developed to diagnose AS with the modified New York (mNY) criteria requiring the presence of X-Ray evidence of changes in the SI joints along with symptoms and signs of spinal and SI joint arthritis. This strict classification system is one reason for the delay in diagnosing AS. A staggering 50% of people with AS are not diagnosed until five years after symptoms develop. There is no blood test to diagnose AS, but one protein found in the blood known as human leukocyte antigen B27 (HLA-B27) is useful to confirm the diagnosis when associated arthritic symptoms are present. Range of motion evaluation, lumbar flexion tests, chest expansion measurements, chin-brow tests, and neurologic testing are all part of the diagnostic process in AS.
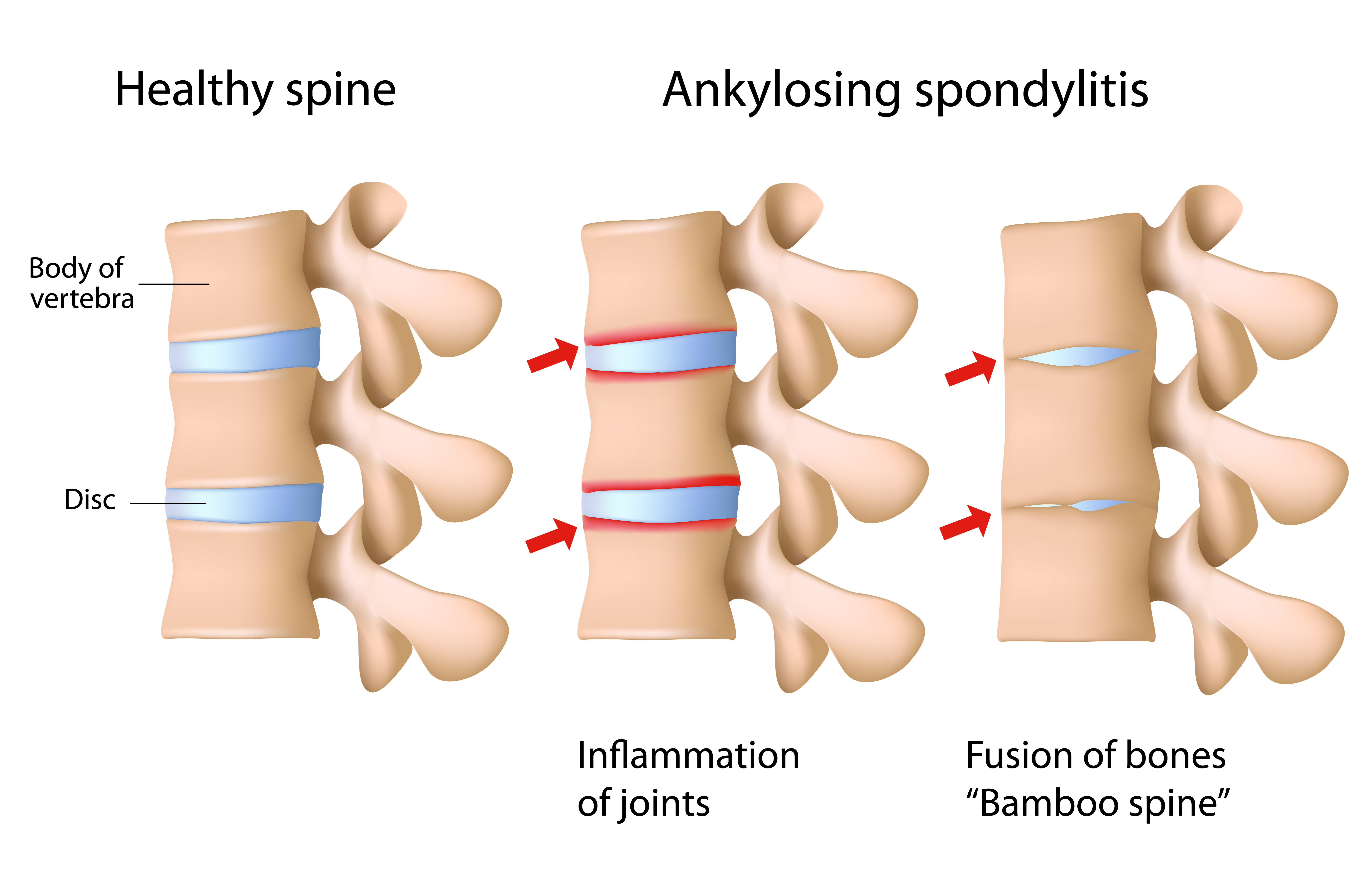
Symptoms and Prevalence of Ankylosing Spondylitis
The disease is more common in men and usually strikes before the age of 40. Stiffness, aching joints, joints that have lost range of motion (such as bending over or getting out of a chair) are all familiar symptoms. Mobility helps relieve the symptoms, while prolonged sitting or lying down usually aggravate the symptoms. The upper spine and neck become stiff and over time can result in a posture deformity known as kyphosis which is a humped over position with the neck and head pushed forward or downward. Kyphosis is due to permanently fused spinal bones. The damage to the cartilage between the breastbone and ribs can result in pain with breathing and decreased chest expansion.
Shoulder joints can be affected as well. Fatigue and loss of appetite are other symptoms of this chronic disease.
Shoulder joints can be affected as well. Fatigue and loss of appetite are other symptoms of this chronic disease.
Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Conventional Treatments
Early treatment can help prevent or delay irreversible damage to the joints. Ibuprofen and naproxen are two nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) that are used to help ease swelling and joint pain. Steroids such as prednisone or prednisolone can reduce the inflammation that causes the pain. Rheumatologists may prescribe DMARDs or disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Methotrexate and sulfasalazine are two such DMARDS. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blockers or biologics from living cells such as Enbrel help the immune system counteract the inflammatory response that leads to disease progression. However, TNF blockers can make a person more susceptible to bacterial, fungal, and viral infections.
Regenerative Therapies Targeted regenerative stem cell therapies and supportive therapies can be used to treat damaged spinal joints and help reset autoimmune function (if applicable). These treatments are non-invasive and can improve quality of life.
Regenerative Therapies Targeted regenerative stem cell therapies and supportive therapies can be used to treat damaged spinal joints and help reset autoimmune function (if applicable). These treatments are non-invasive and can improve quality of life.
When Surgery can be Required
In the rare case of surgery for AS complications, there are four reasons to perform specific surgeries such as osteotomy (removal of bone), decompression (release excess pressure on spinal cord), spinal rod placement and fusion. They are:
- The spinal deformity results in a fixed forward flexed position such as the chin on the chest that prevents the person from eating, looking up, or driving.
- An unstable spine that it moves so much that the joints cannot control spine motion.
- A sensory (pain, tingling) or motor (weakness) nerve defect.
- A combination of any of these.
Surgery & Treatment for Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS)
At Spine Connection we have regenerative and surgical treatments for all spine conditions. As every case is unique we encourage you to receive and compare opinions from our Neurosurgeon and Orthopedic Spine Specialists. We are here to help.
Begin My Assessment
Ask Our Doctors
Join Our Youtube Channel
Watch videos showcasing the latest technologies and surgery techniques, and keep up to date with patient stories from around the globe.