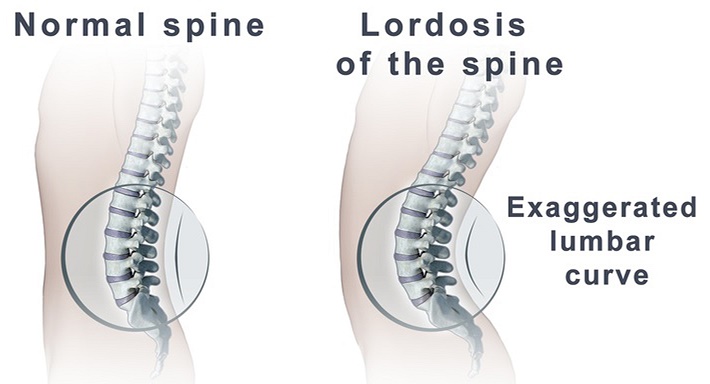
Bad posture is a common cause of hyperlordosis. Other factors that may contribute to hyperlordosis are:
- obesity
- wearing high-heeled shoes for extended periods
- spinal injury
- pregnancy
- neuromuscular diseases
- spondylolisthesis
- osteoporosis
- rickets
- sitting or standing for extended periods
- achondroplasia (dwarfism)
- weak core muscles
A simple test can check your posture: Stand up against straight with your back pushed against the wall. With legs shoulder-width, your head, shoulder blades, and buttocks against the wall. Then, place your hand behind the lower spine. If you can place more than one hand between the back and the wall, then you have hyperlordosis.